24 Solar Terms (二十四节气) {YEAR}
The 24 Solar Terms are a traditional East Asian system that divides the solar year into 24 segments, with each approximately 15 days long. Originating in ancient China over 2,000 years ago, these terms were created by farmers to guide agricultural activities and reflect changes in climate, natural phenomena, and other aspects of life. The “24 Solar Terms” was recognised and added to the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization’s (UNESCO) World Intangible Cultural Heritage List on 11 November, 2016.
This system provides a framework for understanding seasonal changes, guiding agricultural activities, and daily life in East Asian cultures, including Japan, Korea, and Vietnam. They are still widely used in East Asian and some Southeast Asian countries today.
| Solar Term | Date | Description |
|---|
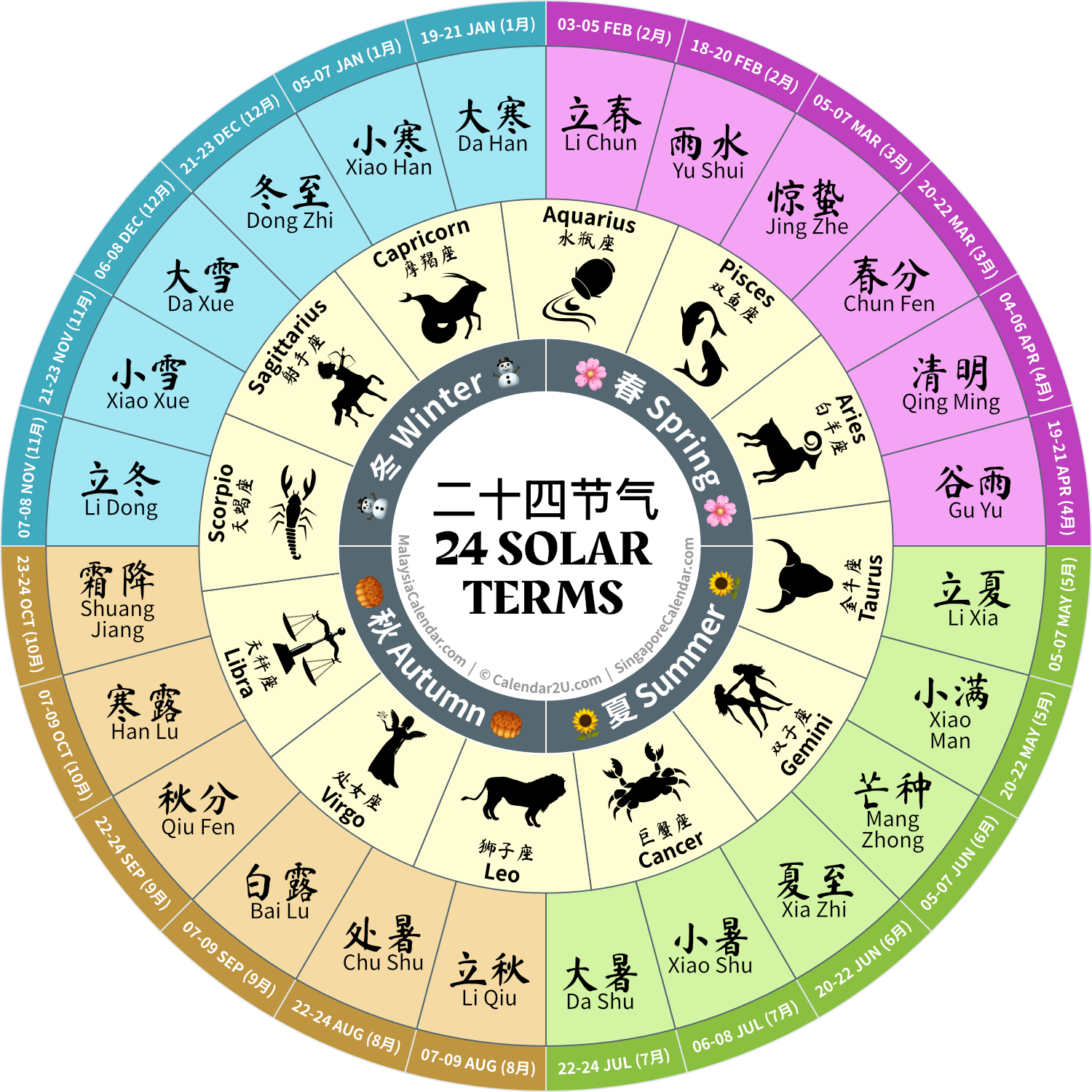
Each solar term is closely aligned with natural phenomena and agricultural rhythms, with names that describe weather patterns, growth stages of plants, or other seasonal characteristics. The 24 terms are divided into four seasons:
Spring Terms
Spring terms focus on the renewal of life, warming weather, and increased rainfall, setting the stage for growth and agricultural activities.
- 立春 (Li Chun - Beginning of Spring)
- 雨水 (Yu Shui - Spring Showers)
- 惊蛰 (Jing Zhe - Awakening of Insects)
- 春分 (Chun Fen - Spring Equinox)
- 清明 (Qing Ming - Clear and Bright)
- 谷雨 (Gu Yu - Grain Rain)
Summer Terms
The summer terms highlight the intense warmth, agricultural growth, and, later, harvest periods, with plenty of rainfall supporting plant development.
- 立夏 (Li Xia - Beginning of Summer)
- 小满 (Xiao Man - Grain Buds)
- 芒种 (Mang Zhong - Grain in Ear)
- 夏至 (Xia Zhi - Summer Solstice)
- 小暑 (Xiao Shu - Minor Heat)
- 大暑 (Da Shu - Major Heat)
Autumn Terms
Autumn terms mark cooling weather, harvest times, and the shift toward shorter days as the year progresses toward winter.
- 立秋 (Li Qiu - Beginning of Autumn)
- 处暑 (Chu Shu - End of Heat)
- 白露 (Bai Lu - White Dew)
- 秋分 (Qiu Fen - Autumn Equinox)
- 寒露 (Han Lu - Cold Dew)
- 霜降 (Shuang Jiang - Descent of Frost)
Winter Terms
Winter terms emphasize cold weather, the dormant phase of nature, and practices to stay warm and healthy through the season.
- 立冬 (Li Dong - Beginning of Winter)
- 小雪 (Xiao Xue - Minor Snow)
- 大雪 (Da Xue - Major Snow)
- 冬至 (Dong Zhi - Winter Solstice)
- 小寒 (Xiao Han - Moderate Cold)
- 大寒 (Da Han - Greater Cold)